Pixiv - 蒼ஐ/お仕事募集中
2949 字
15 分钟
2025.12.09 C语言程序设计上机实习六
2025.12.09 C语言程序设计上机实习六
必做题
选做题
题目源文件实验六.pdf
题目1:动态字符串数组的双重排序
void SortStrings(char **strs, int n){
if (strs == NULL || n <= 0) // 传入失败或字符串小于等于0则退出函数 { return; }
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) // 对第i个字符串进行操作 { int len = strlen(strs[i]); // 冒泡排序 for (int j = 0; j < len - 1; j++) { for (int k = j + 1; k < len; k++) { if (strs[i][j] > strs[i][k]) { char temp = strs[i][j]; strs[i][j] = strs[i][k]; strs[i][k] = temp; } } } }
// 冒泡排序 for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) { for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) { if (strcmp(strs[i], strs[j]) > 0) { char *temp = strs[i]; strs[i] = strs[j]; strs[j] = temp; } } }
}
题目2:模拟解析CSV文件
结构体定义
struct Person { char name[20]; int age; char city[20];};ParseCSV函数
void ParseCSV(const char *csvData, struct Person **persons, int *count){ if (persons == NULL || count == NULL) return;
*persons = NULL; *count = 0;
// 若 csvData 为空或 NULL,则 return if (csvData == NULL || csvData[0] == '\0') { return; }
int len = strlen(csvData); int lines = 0; char *temp = NULL; temp = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * (len + 1)); if (!temp) free(temp); if (temp == NULL) return; memcpy(temp, csvData, len + 1); for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { if (temp[i] == '\n') { lines++; } }
if (len > 0 && temp[len - 1] != '\n') { lines++; }
if (lines == 0) return;
*persons = (struct Person *)malloc(sizeof(struct Person) * lines); if (*persons == NULL) return;
int index = 0; int status = 1;
char *line; char *saveptr = NULL;
line = strtok_r(temp, "\n", &saveptr);
while(line && status) { char *saveptr2 = NULL; char *name = strtok_r(line, ",", &saveptr2); char *ageStr = strtok_r(NULL, ",", &saveptr2); char *city = strtok_r(NULL, ",", &saveptr2); char *extra = strtok_r(NULL, ",", &saveptr2);
if (!name || !ageStr || !city || extra != NULL) { status = 0; break; }
if (strlen(name) == 0 || strlen(name) >= 20) { status = 0; break; }
strcpy((*persons)[index].name, name);
for (int i = 0; ageStr[i]; i++) { if (ageStr[i] < '0' || ageStr[i] > '9') { status = 0; break; } }
if (status == 0) break;
(*persons)[index].age = atoi(ageStr);
if (strlen(city) == 0 || strlen(city) >= 20) { status = 0; break; } strcpy((*persons)[index].city, city);
index++; line = strtok_r(NULL, "\n", &saveptr);
}
free(temp);
if(status == 0 || index == 0) { free(*persons); *persons = NULL; *count = 0; return; }
*count = index;
return;}AI使用声明:
对于库函数strtok,在本程序中会发生共用缓冲区问题,导致测试例1无法通过。
在《C语言程序设计》附录部分仅介绍了strtok。在AI的帮助下了解到更安全的库函数strtok_r,故更换使用后正常。
若不使用strtok与strtor_r,其他的方法其实还有(包括但不限于)
- 逐位读取读到“,”再处理
- 统计“,”在每一行中出现的个数判断格式是否正常
题目3:排序后存储为CSV风格的字符串
//未写待补附:完整代码
TestSortStrings.c
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <string.h>
void SortStrings(char **strs, int n);
// ========== 测试框架 ==========void run_tests();
// ========== 主函数 ==========int main() { run_tests(); return 0;}
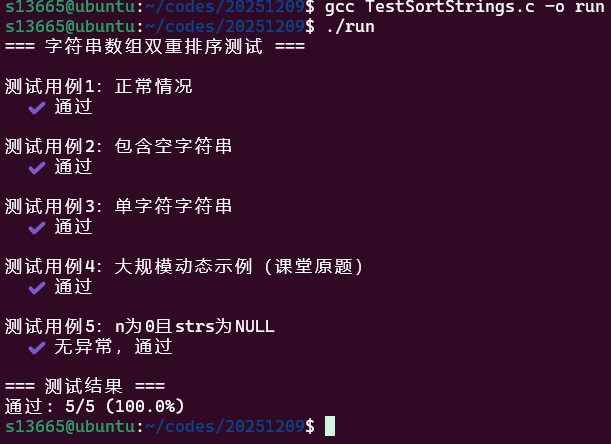
void run_tests(){ printf("=== 字符串数组双重排序测试 ===\n"); int pass_count = 0; int total_count = 0;
// 测试用例1:正常情况 printf("\n测试用例1:正常情况\n"); char *strs1[] = {malloc(4), malloc(4), malloc(4)}; strcpy(strs1[0], "cba"); strcpy(strs1[1], "fed"); strcpy(strs1[2], "abc"); SortStrings(strs1, 3); if (strcmp(strs1[0], "abc") == 0 && strcmp(strs1[1], "abc") == 0 && strcmp(strs1[2], "def") == 0) { printf(" ✔️ 通过\n"); pass_count++; } else { printf(" ❌ 失败: 实际 [%s, %s, %s]\n", strs1[0], strs1[1], strs1[2]); } free(strs1[0]); free(strs1[1]); free(strs1[2]); total_count++;
// 测试用例2:包含空字符串 printf("\n测试用例2:包含空字符串\n"); char *strs2[] = {malloc(1), malloc(5), malloc(6)}; strcpy(strs2[0], ""); strcpy(strs2[1], "dcba"); strcpy(strs2[2], "hello"); SortStrings(strs2, 3); if (strcmp(strs2[0], "") == 0 && strcmp(strs2[1], "abcd") == 0 && strcmp(strs2[2], "ehllo") == 0) { printf(" ✔️ 通过\n"); pass_count++; } else { printf(" ❌ 失败\n"); } free(strs2[0]); free(strs2[1]); free(strs2[2]); total_count++;
// 测试用例3:单字符字符串 printf("\n测试用例3:单字符字符串\n"); char *strs3[] = {malloc(2), malloc(2), malloc(2)}; strcpy(strs3[0], "b"); strcpy(strs3[1], "a"); strcpy(strs3[2], "c"); SortStrings(strs3, 3); if (strcmp(strs3[0], "a") == 0 && strcmp(strs3[1], "b") == 0 && strcmp(strs3[2], "c") == 0) { printf(" ✔️ 通过\n"); pass_count++; } else { printf(" ❌ 失败\n"); } free(strs3[0]); free(strs3[1]); free(strs3[2]); total_count++;
// 测试用例4:大规模动态示例(课堂原题) printf("\n测试用例4:大规模动态示例(课堂原题)\n"); int m = 26; char **strs4 = (char**)malloc(m * sizeof(char*)); for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) { strs4[i] = (char*)malloc((i + 2) * sizeof(char)); for (int j = 0; j <= i; j++) { strs4[i][j] = 'z' - j; } strs4[i][i + 1] = '\0'; }
SortStrings(strs4, m);
int valid = 1; for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) { size_t len = strlen(strs4[i]); for (size_t j = 0; j + 1 < len; j++) { if (strs4[i][j] > strs4[i][j + 1]) { valid = 0; break; } } if (!valid) { break; } }
if (valid) { for (int i = 0; i < m - 1; i++) { if (strcmp(strs4[i], strs4[i + 1]) > 0) { valid = 0; break; } } }
if (valid) { printf(" ✔️ 通过\n"); pass_count++; } else { printf(" ❌ 失败\n"); }
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) { free(strs4[i]); } free(strs4); total_count++;
// 测试用例5:n为0且strs为NULL printf("\n测试用例5:n为0且strs为NULL\n"); SortStrings(NULL, 0); printf(" ✔️ 无异常,通过\n"); pass_count++; total_count++;
printf("\n=== 测试结果 ===\n"); printf("通过: %d/%d (%.1f%%)\n", pass_count, total_count, (float)pass_count / total_count * 100);}
void SortStrings(char **strs, int n){
if (strs == NULL || n <= 0) // 传入失败或字符串小于等于0则退出函数 { return; }
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) // 对第i个字符串进行操作 { int len = strlen(strs[i]); // 冒泡排序 for (int j = 0; j < len - 1; j++) { for (int k = j + 1; k < len; k++) { if (strs[i][j] > strs[i][k]) { char temp = strs[i][j]; strs[i][j] = strs[i][k]; strs[i][k] = temp; } } } }
// 冒泡排序 for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) { for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) { if (strcmp(strs[i], strs[j]) > 0) { char *temp = strs[i]; strs[i] = strs[j]; strs[j] = temp; } } }
}TestParseCSV.c
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <string.h>
struct Person { char name[20]; int age; char city[20];};
void ParseCSV(const char *csvData, struct Person **persons, int *count);
// ========== 测试框架 ==========void run_tests();
// ========== 主函数 ==========int main(){ run_tests(); return 0;}
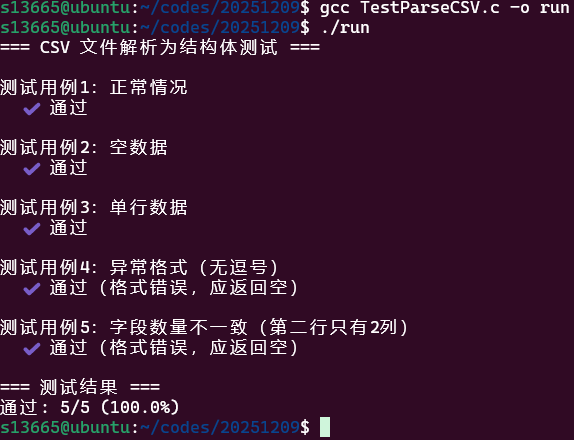
void run_tests(){ printf("=== CSV 文件解析为结构体测试 ===\n"); int pass_count = 0; int total_count = 0;
// 测试用例1:正常情况 printf("\n测试用例1:正常情况\n"); const char *csv1 = "Zoe,29,Hangzhou\nAlice,25,Beijing\nBob,30,Shanghai\nCharlie,22,Guangzhou\nDiana,28,Shenzhen";
struct Person *persons1 = NULL; int count1 = 0;
ParseCSV(csv1, &persons1, &count1);
if (count1 == 5) { if (strcmp(persons1[0].name, "Zoe") == 0 && persons1[0].age == 29 && strcmp(persons1[0].city, "Hangzhou") == 0) { if (strcmp(persons1[1].name, "Alice") == 0 && persons1[1].age == 25 && strcmp(persons1[1].city, "Beijing") == 0) { if (strcmp(persons1[2].name, "Bob") == 0 && persons1[2].age == 30 && strcmp(persons1[2].city, "Shanghai") == 0) { if (strcmp(persons1[3].name, "Charlie") == 0 && persons1[3].age == 22 && strcmp(persons1[3].city, "Guangzhou") == 0) { if (strcmp(persons1[4].name, "Diana") == 0 && persons1[4].age == 28 && strcmp(persons1[4].city, "Shenzhen") == 0) { printf(" ✔️ 通过\n"); pass_count++; } else { printf(" ❌ 失败: Diana 行错误\n"); } } else { printf(" ❌ 失败: Charlie 行错误\n"); } } else { printf(" ❌ 失败: Bob 行错误\n"); } } else { printf(" ❌ 失败: Alice 行错误\n"); } } else { printf(" ❌ 失败: Zoe 行错误\n"); } } else { printf(" ❌ 失败: 记录数不正确,期望 5,实际 %d\n", count1); }
free(persons1); total_count++;
// 测试用例2:空数据 printf("\n测试用例2:空数据\n"); const char *empty = ""; struct Person *persons2 = NULL; int count2 = 0;
ParseCSV(empty, &persons2, &count2);
if (count2 == 0 && persons2 == NULL) { printf(" ✔️ 通过\n"); pass_count++; } else { printf(" ❌ 失败\n"); } total_count++;
// 测试用例3:单行 printf("\n测试用例3:单行数据\n"); const char *single = "Tom,35,Chengdu"; struct Person *persons3 = NULL; int count3 = 0;
ParseCSV(single, &persons3, &count3);
if (count3 == 1 && strcmp(persons3[0].name, "Tom") == 0 && persons3[0].age == 35 && strcmp(persons3[0].city, "Chengdu") == 0) { printf(" ✔️ 通过\n"); pass_count++; } else { printf(" ❌ 失败\n"); }
free(persons3); total_count++;
// 测试用例4:无逗号 printf("\n测试用例4:异常格式(无逗号)\n"); const char *invalid = "John18NewYork\nMary22Paris"; struct Person *persons4 = NULL; int count4 = 0;
ParseCSV(invalid, &persons4, &count4); if (count4 == 0 && persons4 == NULL) { printf(" ✔️ 通过(格式错误,应返回空)\n"); pass_count++; } else { printf(" ❌ 失败:应拒绝解析\n"); } total_count++;
// 测试用例5:字段数量不一致(某行不是3列) printf("\n测试用例5:字段数量不一致(第二行只有2列)\n"); const char *csv5 = "Zoe,29,Hangzhou\nAlice,25\nBob,30,Shanghai"; struct Person *persons5 = NULL; int count5 = 0;
ParseCSV(csv5, &persons5, &count5);
if (count5 == 0 && persons5 == NULL) { printf(" ✔️ 通过(格式错误,应返回空)\n"); pass_count++; } else { printf(" ❌ 失败:应拒绝解析\n"); } total_count++;
// 汇总结果 printf("\n=== 测试结果 ===\n"); printf("通过: %d/%d (%.1f%%)\n", pass_count, total_count, (float)pass_count / total_count * 100);}
void ParseCSV(const char *csvData, struct Person **persons, int *count){ if (persons == NULL || count == NULL) return;
*persons = NULL; *count = 0;
// 若 csvData 为空或 NULL,则 return if (csvData == NULL || csvData[0] == '\0') { return; }
int len = strlen(csvData); int lines = 0; char *temp = NULL; temp = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * (len + 1)); if (!temp) free(temp); if (temp == NULL) return; memcpy(temp, csvData, len + 1); for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { if (temp[i] == '\n') { lines++; } }
if (len > 0 && temp[len - 1] != '\n') { lines++; }
if (lines == 0) return;
*persons = (struct Person *)malloc(sizeof(struct Person) * lines); if (*persons == NULL) return;
int index = 0; int status = 1;
char *line; char *saveptr = NULL;
line = strtok_r(temp, "\n", &saveptr);
while(line && status) { char *saveptr2 = NULL; char *name = strtok_r(line, ",", &saveptr2); char *ageStr = strtok_r(NULL, ",", &saveptr2); char *city = strtok_r(NULL, ",", &saveptr2); char *extra = strtok_r(NULL, ",", &saveptr2);
if (!name || !ageStr || !city || extra != NULL) { status = 0; break; }
if (strlen(name) == 0 || strlen(name) >= 20) { status = 0; break; }
strcpy((*persons)[index].name, name);
for (int i = 0; ageStr[i]; i++) { if (ageStr[i] < '0' || ageStr[i] > '9') { status = 0; break; } }
if (status == 0) break;
(*persons)[index].age = atoi(ageStr);
if (strlen(city) == 0 || strlen(city) >= 20) { status = 0; break; } strcpy((*persons)[index].city, city);
index++; line = strtok_r(NULL, "\n", &saveptr);
}
free(temp);
if(status == 0 || index == 0) { free(*persons); *persons = NULL; *count = 0; return; }
*count = index;
return;}TestSortSaveAsCSV.c
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <string.h>#include <malloc.h>
#define MAX_MALLOC 100
char *SortSaveAsCSV(struct Person *persons, int count);
// =================== 测试框架 ===================void run_tests();
int main(){ run_tests(); return 0;}
void run_tests(){ printf("=== 排序后存储为CSV风格字符串测试 ===\n"); int pass_count = 0; int total_count = 0;
// 测试用例1:正常情况(多个人,不同年龄) printf("\n测试用例1:正常情况\n"); struct Person people1[] = { (struct Person){"Zoe", 29, "Hangzhou"}, (struct Person){"Alice", 25, "Beijing"}, (struct Person){"Bob", 30, "Shanghai"} }; char *csv1 = SortSaveAsCSV(people1, 3);
if (csv1 != NULL && strcmp(csv1, "Alice,25,Beijing\nZoe,29,Hangzhou\nBob,30,Shanghai\n") == 0 && malloc_usable_size(csv1) < MAX_MALLOC) { printf(" ✔️ 通过\n"); pass_count++; } else { printf(" ❌ 失败:输出不正确or内存开辟过大\n"); } free(csv1); total_count++;
// 测试用例2:空数组或NULL输入 printf("\n测试用例2:空数组或NULL输入\n"); char *csv2 = SortSaveAsCSV(NULL, 0); if (strlen(csv2) == 0) { printf(" ✔️ 通过\n"); pass_count++; } else { printf(" ❌ 失败:应返回空字符串\n"); } total_count++;
// 测试用例3:单个元素 printf("\n测试用例3:单个元素\n"); struct Person person3 = (struct Person){"Tom", 35, "Chengdu"}; char *csv3 = SortSaveAsCSV(&person3, 1); if (csv3 != NULL && strcmp(csv3, "Tom,35,Chengdu\n") == 0 && malloc_usable_size(csv3) < MAX_MALLOC) { printf(" ✔️ 通过\n"); pass_count++; } else { printf(" ❌ 失败:单行输出错误或开辟内存过大\n"); } free(csv3); total_count++;
// 测试用例4:相同年龄(稳定排序) printf("\n测试用例4:相同年龄(稳定排序)\n"); struct Person people4[] = { (struct Person){"Zoe", 25, "Hangzhou"}, (struct Person){"Alice", 25, "Beijing"}, (struct Person){"Bob", 26, "Shanghai"} }; char *csv4 = SortSaveAsCSV(people4, 3); if (csv4 != NULL && strcmp(csv4, "Zoe,25,Hangzhou\nAlice,25,Beijing\nBob,26,Shanghai\n") == 0 && malloc_usable_size(csv4) < MAX_MALLOC) { printf(" ✔️ 通过\n"); pass_count++; } else { printf(" ❌ 失败:排序不稳定或式格错误or开辟内存过大\n"); } free(csv4); total_count++;
// 测试用例5:城市为空字符串 printf("\n测试用例5:城市为空字符串\n"); struct Person people5[] = { (struct Person){"Zoe", 29, ""}, (struct Person){"Alice", 25, "Beijing"} }; char *csv5 = SortSaveAsCSV(people5, 2); if (csv5 != NULL && strcmp(csv5, "Alice,25,Beijing\nZoe,29,\n") == 0 && malloc_usable_size(csv5) < MAX_MALLOC) { printf(" ✔️ 通过\n"); pass_count++; } else { printf(" ❌ 失败:空城市未正确处理或内存开辟过大\n"); } free(csv5); total_count++;
// 测试用例6:姓名或城市含特殊字符 printf("\n测试用例6:姓名/城市含特殊字符\n"); struct Person people6[] = { (struct Person){"Li_42", 29, "New-York"}, (struct Person){"OOP_Programmer", 25, "San-Francisco"} }; char *csv6 = SortSaveAsCSV(people6, 2); if (csv6 != NULL && strcmp(csv6, "OOP_Programmer,25,San-Francisco\nLi_42,29,New-York\n") == 0 && malloc_usable_size(csv6) < MAX_MALLOC) { printf(" ✔️ 通过\n"); pass_count++; } else { printf(" ❌ 失败:特殊字符未原样输出或内存开辟过大\n"); } free(csv6); total_count++;
// 测试用例7:负年龄 printf("\n测试用例7:负年龄\n"); struct Person people7[] = { (struct Person){"Zoe", -5, "Hangzhou"}, (struct Person){"Alice", 100, "Beijing"} }; char *csv7 = SortSaveAsCSV(people7, 2); if (csv7 != NULL && strcmp(csv7, "Zoe,-5,Hangzhou\nAlice,100,Beijing\n") == 0 && malloc_usable_size(csv7) < MAX_MALLOC) { printf(" ✔️ 通过\n"); pass_count++; } else { printf(" ❌ 失败:负数年龄未正确输出或内存开辟过大\n"); } free(csv7); total_count++;
// 汇总结果 printf("\n=== 测试结果 ===\n"); printf("通过: %d/%d (%.1f%%)\n", pass_count, total_count, (float)pass_count / total_count * 100);}
//未写待补文章分享
如果这篇文章对你有帮助,欢迎分享给更多人!
2025.12.09 C语言程序设计上机实习六
https://mjy.js.org/posts/20251209-c语言程序设计上机实习六/ 
