Pixiv - 蒼ஐ/お仕事募集中
5436 字
27 分钟
2025.12.02 C语言程序设计上机实习五
2025.12.02 C语言程序设计上机实习五
必做题
选做题
题目源文件实验五.pdf
题目1:字符串查找函数
int FindSubstring(const char* str, const char* substr){ if (!str || !substr) return -1;
int n = strlen(str); int m = strlen(substr);
if (m == 0) return 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= n - m; i++) { int j = 0; while (j < m && str[i + j] == substr[j]) { j++; } if (j == m) { return 1; } }
return 0;}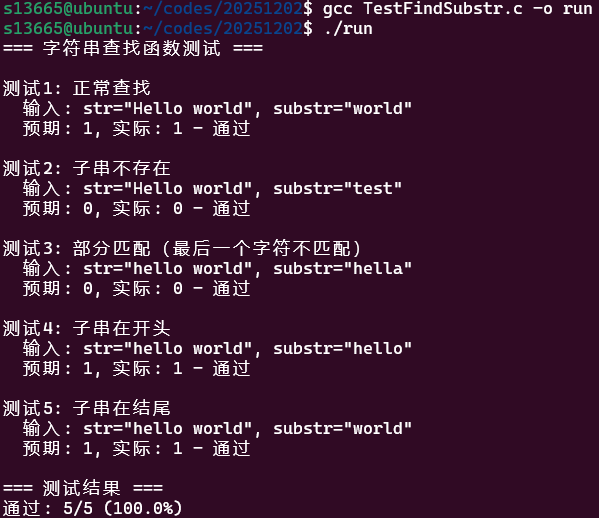
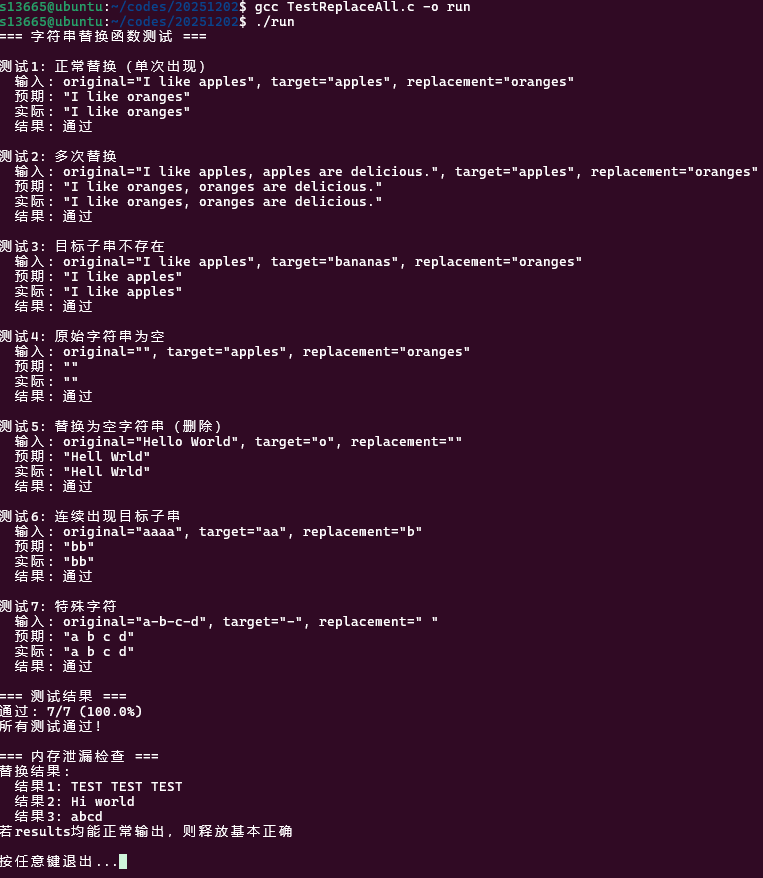
题目2:字符串替换函数
// 字符串替换函数实现char* ReplaceAll(const char* original, const char* target, const char* replacement){ // 检查参数是否为空 if (original == NULL || target == NULL || replacement == NULL) { return NULL; }
// 计算各字符串长度 int orig_len = strlen(original); int target_len = strlen(target); int repl_len = strlen(replacement);
// 如果目标字符串为空,返回原字符串的副本 if (target_len == 0) { char* result = (char*)malloc((orig_len + 1)*sizeof(char));
if (result == NULL) { return NULL; }
strcpy(result, original); result[orig_len] = '\0'; return result; }
// 计算需要替换的次数 int count = 0; const char* pos = original;
while ((pos = strstr(pos, target)) != NULL) // strstr的用法在课本P486 { count++; pos += target_len; // 跳过已找到的目标字符串 }
// 计算新字符串长度 int new_len = orig_len + count * (repl_len - target_len); char* result = (char*)malloc((new_len + 1)*sizeof(char));
if (result == NULL) { return NULL; }
// 执行替换操作 char* current = result; const char* start = original; const char* found;
while ((found = strstr(start, target)) != NULL) { // 复制目标字符串之前的部分 int prefix_len = found - start; if (prefix_len > 0) { strncpy(current, start, prefix_len); current += prefix_len; }
// 复制替换字符串 if (repl_len > 0) { strcpy(current, replacement); current += repl_len; }
// 移动到下一个位置 start = found + target_len; }
// 复制剩余部分 strcpy(current, start); result[new_len] = '\0'; return result;}修改部分:
- malloc用法,长度*sizeof(类型)
- strcpy复制位置(原有-1删去)(两处)
- result字符串末尾要加 ‘\0’ (两处)
- (无用)加入 repl_len > 0 判断
题目3:回文单词检测函数
int HasPalindromeWord(const char* sentence){ if (sentence == NULL) return -1; // 传空参数处理
const char* p = sentence; while (*p) {
while (*p && !isalnum(*p)) // 字母与数字可过,略过字符 { p++; }
if (*p == '\0') // 如果因为上一个while跳到结尾了就该抓紧终止了 { break; }
const char* start = p;
while (*p && isalnum(*p)) // 来个字母和数字作为起点,读到不是字母和数字和'\0'就停 { p++; } const char* end = p;
unsigned int len = end - start; if (len >= 2) { size_t i = 0, j = len - 1; int is_pal = 1; while (i < j) { char a = (char)tolower(start[i]); char b = (char)tolower(start[j]); if (a != b) { is_pal = 0; break; } i++; j--; } if (is_pal) return 1; } }
return 0;}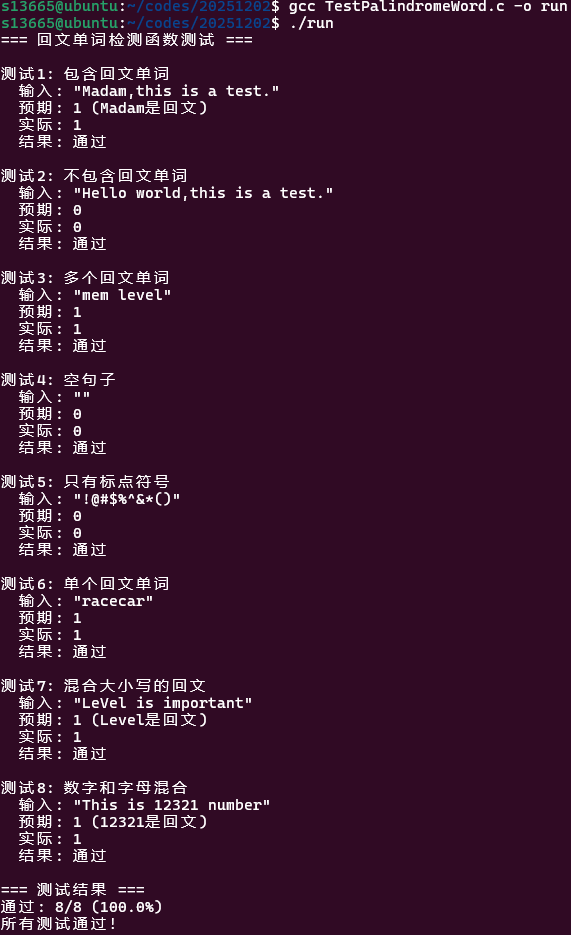
题目4:礼貌数判断函数(被放弃的期中考试题)
int IsPoliteNumber(int n){ int test = n, sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= test; i++) { for (int j = i; j < test; j++) { sum += j; if (sum == test) { return 1; } else if (sum > test) { break; } } sum = 0; } return 0;}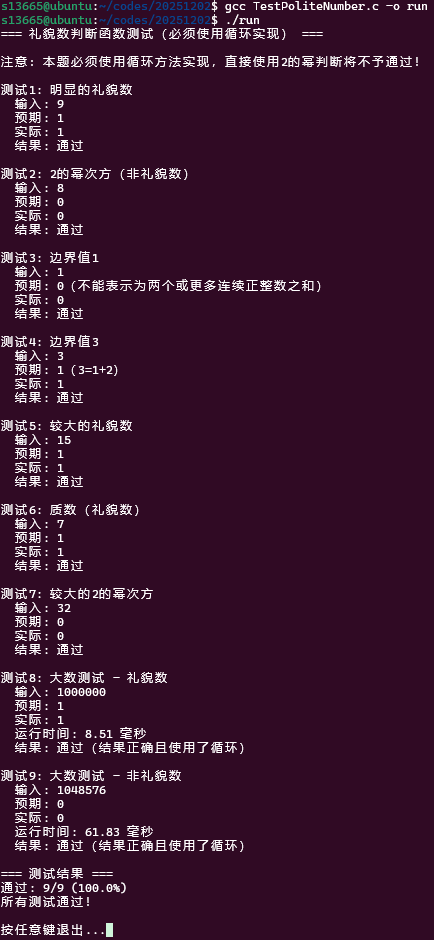
题目5:矩阵转置函数
int** TransMat(int** matrix, int m, int n){ int **arr; arr = (int **)malloc(n * sizeof(int *)); for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { arr[i] = (int *)malloc(m * sizeof(int)); if(arr[i] == NULL) return NULL; for(int j = 0; j < m; j++) { arr[i][j] = matrix[j][i]; } } return arr;}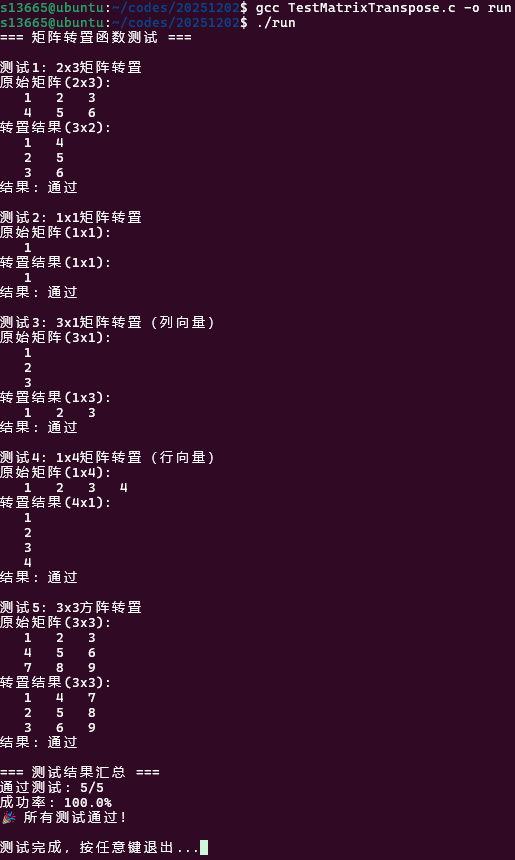
附:完整代码
TestFindSubstr.c
#include <stdio.h>#include <string.h>
// 字符串查找函数声明int FindSubstring(const char* str, const char* substr);// 测试函数void run_tests();
int main() { run_tests(); return 0;}
// 测试函数void run_tests(){ printf("=== 字符串查找函数测试 ===\n\n");
int pass_count = 0; int total_count = 0;
// 测试用例1:正常情况 printf("测试1: 正常查找\n"); int result1 = FindSubstring("Hello world", "world"); int expected1 = 1; printf(" 输入: str=\"Hello world\", substr=\"world\"\n"); printf(" 预期: %d, 实际: %d - %s\n", expected1, result1, result1 == expected1 ? "通过" : "失败"); if (result1 == expected1) pass_count++; total_count++;
// 测试用例2:不存在的情况 printf("\n测试2: 子串不存在\n"); int result2 = FindSubstring("Hello world", "test"); int expected2 = 0; printf(" 输入: str=\"Hello world\", substr=\"test\"\n"); printf(" 预期: %d, 实际: %d - %s\n", expected2, result2, result2 == expected2 ? "通过" : "失败"); if (result2 == expected2) pass_count++; total_count++;
// 测试用例3:部分匹配但最后一个字符不匹配 printf("\n测试3: 部分匹配(最后一个字符不匹配)\n"); int result3 = FindSubstring("hello world", "hella"); int expected3 = 0; printf(" 输入: str=\"hello world\", substr=\"hella\"\n"); printf(" 预期: %d, 实际: %d - %s\n", expected3, result3, result3 == expected3 ? "通过" : "失败"); if (result3 == expected3) pass_count++; total_count++;
// 测试用例4:开头匹配 printf("\n测试4: 子串在开头\n"); int result4 = FindSubstring("hello world", "hello"); int expected4 = 1; printf(" 输入: str=\"hello world\", substr=\"hello\"\n"); printf(" 预期: %d, 实际: %d - %s\n", expected4, result4, result4 == expected4 ? "通过" : "失败"); if (result4 == expected4) pass_count++; total_count++;
// 测试用例5:结尾匹配 printf("\n测试5: 子串在结尾\n"); int result5 = FindSubstring("hello world", "world"); int expected5 = 1; printf(" 输入: str=\"hello world\", substr=\"world\"\n"); printf(" 预期: %d, 实际: %d - %s\n", expected5, result5, result5 == expected5 ? "通过" : "失败"); if (result5 == expected5) pass_count++; total_count++;
// 汇总结果 printf("\n=== 测试结果 ===\n"); printf("通过: %d/%d (%.1f%%)\n", pass_count, total_count, (float)pass_count/total_count*100);}
int FindSubstring(const char* str, const char* substr){ if (!str || !substr) return -1;
int n = strlen(str); int m = strlen(substr);
if (m == 0) return 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= n - m; i++) { int j = 0; while (j < m && str[i + j] == substr[j]) { j++; } if (j == m) { return 1; } }
return 0;}TestReplaceAll.c
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <string.h>
// 函数原型声明char* ReplaceAll(const char* original, const char* target, const char* replacement);int StringsEqual(const char* str1, const char* str2);void RunTests();void TestMemoryLeak();
int main(){ RunTests(); TestMemoryLeak();
printf("\n按任意键退出..."); getchar();
return 0;}
// 辅助函数:比较两个字符串是否相等int StringsEqual(const char* str1, const char* str2){ if (str1 == NULL && str2 == NULL) { return 1; }
if (str1 == NULL || str2 == NULL) { return 0; }
return strcmp(str1, str2) == 0;}
// 测试函数void RunTests(){ printf("=== 字符串替换函数测试 ===\n\n");
int pass_count = 0; int total_count = 0; char* result = NULL; char* expected = NULL;
// 测试用例1:正常情况 - 单次替换 printf("测试1: 正常替换(单次出现)\n"); result = ReplaceAll("I like apples", "apples", "oranges"); expected = "I like oranges"; printf(" 输入: original=\"I like apples\", target=\"apples\", replacement=\"oranges\"\n"); printf(" 预期: \"%s\"\n", expected); printf(" 实际: \"%s\"\n", result ? result : "NULL"); printf(" 结果: %s\n", StringsEqual(result, expected) ? "通过" : "失败");
if (StringsEqual(result, expected)) { pass_count++; } total_count++; result = NULL;
// 测试用例2:多次替换 printf("\n测试2: 多次替换\n"); result = ReplaceAll("I like apples, apples are delicious.", "apples", "oranges"); expected = "I like oranges, oranges are delicious."; printf(" 输入: original=\"I like apples, apples are delicious.\", target=\"apples\", replacement=\"oranges\"\n"); printf(" 预期: \"%s\"\n", expected); printf(" 实际: \"%s\"\n", result ? result : "NULL"); printf(" 结果: %s\n", StringsEqual(result, expected) ? "通过" : "失败");
if (StringsEqual(result, expected)) { pass_count++; } total_count++; result = NULL;
// 测试用例3:目标子串不存在 printf("\n测试3: 目标子串不存在\n"); result = ReplaceAll("I like apples", "bananas", "oranges"); expected = "I like apples"; printf(" 输入: original=\"I like apples\", target=\"bananas\", replacement=\"oranges\"\n"); printf(" 预期: \"%s\"\n", expected); printf(" 实际: \"%s\"\n", result ? result : "NULL"); printf(" 结果: %s\n", StringsEqual(result, expected) ? "通过" : "失败");
if (StringsEqual(result, expected)) { pass_count++; } total_count++; result = NULL;
// 测试用例4:原始字符串为空 printf("\n测试4: 原始字符串为空\n"); result = ReplaceAll("", "apples", "oranges"); expected = ""; printf(" 输入: original=\"\", target=\"apples\", replacement=\"oranges\"\n"); printf(" 预期: \"%s\"\n", expected); printf(" 实际: \"%s\"\n", result ? result : "NULL"); printf(" 结果: %s\n", StringsEqual(result, expected) ? "通过" : "失败");
if (StringsEqual(result, expected)) { pass_count++; } total_count++; result = NULL;
// 测试用例5:替换为空字符串(删除操作) printf("\n测试5: 替换为空字符串(删除)\n"); result = ReplaceAll("Hello World", "o", ""); expected = "Hell Wrld"; printf(" 输入: original=\"Hello World\", target=\"o\", replacement=\"\"\n"); printf(" 预期: \"%s\"\n", expected); printf(" 实际: \"%s\"\n", result ? result : "NULL"); printf(" 结果: %s\n", StringsEqual(result, expected) ? "通过" : "失败");
if (StringsEqual(result, expected)) { pass_count++; } total_count++; result = NULL;
// 测试用例6:连续出现目标子串(重点测试) printf("\n测试6: 连续出现目标子串\n"); result = ReplaceAll("aaaa", "aa", "b"); expected = "bb"; printf(" 输入: original=\"aaaa\", target=\"aa\", replacement=\"b\"\n"); printf(" 预期: \"%s\"\n", expected); printf(" 实际: \"%s\"\n", result ? result : "NULL"); printf(" 结果: %s\n", StringsEqual(result, expected) ? "通过" : "失败");
if (StringsEqual(result, expected)) { pass_count++; } total_count++; result = NULL;
// 测试用例7:特殊字符 printf("\n测试7: 特殊字符\n"); result = ReplaceAll("a-b-c-d", "-", " "); expected = "a b c d"; printf(" 输入: original=\"a-b-c-d\", target=\"-\", replacement=\" \"\n"); printf(" 预期: \"%s\"\n", expected); printf(" 实际: \"%s\"\n", result ? result : "NULL"); printf(" 结果: %s\n", StringsEqual(result, expected) ? "通过" : "失败");
if (StringsEqual(result, expected)) { pass_count++; } total_count++; result = NULL;
// 汇总结果 printf("\n=== 测试结果 ===\n"); printf("通过: %d/%d (%.1f%%)\n", pass_count, total_count, (float)pass_count / total_count * 100);
if (pass_count == total_count) { printf("所有测试通过!\n"); } else { printf("有 %d 个测试失败\n", total_count - pass_count); }}
// 内存泄漏检查辅助函数void TestMemoryLeak(){ printf("\n=== 内存泄漏检查 ===\n");
// 测试多次替换,检查是否有内存泄漏 char* results[3];
results[0] = ReplaceAll("test test test", "test", "TEST"); results[1] = ReplaceAll("hello world", "hello", "Hi"); results[2] = ReplaceAll("a b c d", " ", "");
printf("替换结果:\n");
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { printf(" 结果%d: %s\n", i + 1, results[i] ? results[i] : "NULL"); free(results[i]); // 正确释放内存 results[i] = NULL; }
printf("若results均能正常输出,则释放基本正确\n");}
// 字符串替换函数实现char* ReplaceAll(const char* original, const char* target, const char* replacement){ // 检查参数是否为空 if (original == NULL || target == NULL || replacement == NULL) { return NULL; }
// 计算各字符串长度 int orig_len = strlen(original); int target_len = strlen(target); int repl_len = strlen(replacement);
// 如果目标字符串为空,返回原字符串的副本 if (target_len == 0) { char* result = (char*)malloc((orig_len + 1)*sizeof(char));
if (result == NULL) { return NULL; }
strcpy(result, original); result[orig_len] = '\0'; return result; }
// 计算需要替换的次数 int count = 0; const char* pos = original;
while ((pos = strstr(pos, target)) != NULL) // strstr的用法在课本P486 { count++; pos += target_len; // 跳过已找到的目标字符串 }
// 计算新字符串长度 int new_len = orig_len + count * (repl_len - target_len); char* result = (char*)malloc((new_len + 1)*sizeof(char));
if (result == NULL) { return NULL; }
// 执行替换操作 char* current = result; const char* start = original; const char* found;
while ((found = strstr(start, target)) != NULL) { // 复制目标字符串之前的部分 int prefix_len = found - start; if (prefix_len > 0) { strncpy(current, start, prefix_len); current += prefix_len; }
// 复制替换字符串 if (repl_len > 0) { strcpy(current, replacement); current += repl_len; }
// 移动到下一个位置 start = found + target_len; }
// 复制剩余部分 strcpy(current, start); result[new_len] = '\0'; return result;}TestPalindromeWord.c
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <ctype.h>
// 函数原型声明int HasPalindromeWord(const char* sentence);void RunTests();
int main(){ RunTests(); printf("\n按任意键退出..."); getchar(); return 0;}
// 测试函数void RunTests(){ printf("=== 回文单词检测函数测试 ===\n\n");
int pass_count = 0; int total_count = 0; int result = 0;
// 测试用例1:包含回文单词 printf("测试1: 包含回文单词\n"); result = HasPalindromeWord("Madam,this is a test."); printf(" 输入: \"Madam,this is a test.\"\n"); printf(" 预期: 1 (Madam是回文)\n"); printf(" 实际: %d\n", result); printf(" 结果: %s\n", result == 1 ? "通过" : "失败");
if (result == 1) pass_count++; total_count++;
// 测试用例2:不包含回文单词 printf("\n测试2: 不包含回文单词\n"); result = HasPalindromeWord("Hello world,this is a test."); printf(" 输入: \"Hello world,this is a test.\"\n"); printf(" 预期: 0\n"); printf(" 实际: %d\n", result); printf(" 结果: %s\n", result == 0 ? "通过" : "失败");
if (result == 0) pass_count++; total_count++;
// 测试用例3:多个回文单词 printf("\n测试3: 多个回文单词\n"); result = HasPalindromeWord("mem level"); printf(" 输入: \"mem level\"\n"); printf(" 预期: 1\n"); printf(" 实际: %d\n", result); printf(" 结果: %s\n", result == 1 ? "通过" : "失败");
if (result == 1) pass_count++; total_count++;
// 测试用例4:空句子 printf("\n测试4: 空句子\n"); result = HasPalindromeWord(""); printf(" 输入: \"\"\n"); printf(" 预期: 0\n"); printf(" 实际: %d\n", result); printf(" 结果: %s\n", result == 0 ? "通过" : "失败");
if (result == 0) pass_count++; total_count++;
// 测试用例5:只有标点符号 printf("\n测试5: 只有标点符号\n"); result = HasPalindromeWord("!@#$%^&*()"); printf(" 输入: \"!@#$%%^&*()\"\n"); printf(" 预期: 0\n"); printf(" 实际: %d\n", result); printf(" 结果: %s\n", result == 0 ? "通过" : "失败");
if (result == 0) pass_count++; total_count++;
// 测试用例6:单个回文单词 printf("\n测试6: 单个回文单词\n"); result = HasPalindromeWord("racecar"); printf(" 输入: \"racecar\"\n"); printf(" 预期: 1\n"); printf(" 实际: %d\n", result); printf(" 结果: %s\n", result == 1 ? "通过" : "失败");
if (result == 1) pass_count++; total_count++;
// 测试用例7:混合大小写的回文 printf("\n测试7: 混合大小写的回文\n"); result = HasPalindromeWord("LeVel is important"); printf(" 输入: \"LeVel is important\"\n"); printf(" 预期: 1 (Level是回文)\n"); printf(" 实际: %d\n", result); printf(" 结果: %s\n", result == 1 ? "通过" : "失败");
if (result == 1) pass_count++; total_count++;
// 测试用例8:数字和字母混合 printf("\n测试8: 数字和字母混合\n"); result = HasPalindromeWord("This is 12321 number"); printf(" 输入: \"This is 12321 number\"\n"); printf(" 预期: 1 (12321是回文)\n"); printf(" 实际: %d\n", result); printf(" 结果: %s\n", result == 1 ? "通过" : "失败");
if (result == 1) pass_count++; total_count++;
// 汇总结果 printf("\n=== 测试结果 ===\n"); printf("通过: %d/%d (%.1f%%)\n", pass_count, total_count, (float)pass_count / total_count * 100);
if (pass_count == total_count) { printf("所有测试通过!\n"); } else { printf("有 %d 个测试失败\n", total_count - pass_count); }}
int HasPalindromeWord(const char* sentence){ if (sentence == NULL) return -1; // 传空参数处理
const char* p = sentence; while (*p) {
while (*p && !isalnum(*p)) // 字母与数字可过,略过字符 { p++; }
if (*p == '\0') // 如果因为上一个while跳到结尾了就该抓紧终止了 { break; }
const char* start = p;
while (*p && isalnum(*p)) // 来个字母和数字作为起点,读到不是字母和数字和'\0'就停 { p++; } const char* end = p;
unsigned int len = end - start; if (len >= 2) { size_t i = 0, j = len - 1; int is_pal = 1; while (i < j) { char a = (char)tolower(start[i]); char b = (char)tolower(start[j]); if (a != b) { is_pal = 0; break; } i++; j--; } if (is_pal) return 1; } }
return 0;}TestPoliteNumber.c
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <time.h>
// 函数原型声明int IsPoliteNumber(int n);void RunTests();
int main(){ RunTests(); printf("\n按任意键退出..."); getchar(); return 0;}
// 测试函数void RunTests(){ printf("=== 礼貌数判断函数测试(必须使用循环实现) ===\n\n"); printf("注意:本题必须使用循环方法实现,直接使用2的幂判断将不予通过!\n\n");
int pass_count = 0; int total_count = 0; int result = 0; clock_t start, end; double cpu_time_used;
// 测试用例1:明显的礼貌数 printf("测试1: 明显的礼貌数\n"); result = IsPoliteNumber(9); // 9 = 4+5 或 2+3+4 printf(" 输入: 9\n"); printf(" 预期: 1\n"); printf(" 实际: %d\n", result); printf(" 结果: %s\n", result == 1 ? "通过" : "失败");
if (result == 1) pass_count++; total_count++;
// 测试用例2:2的幂次方(非礼貌数) printf("\n测试2: 2的幂次方(非礼貌数)\n"); result = IsPoliteNumber(8); // 8 = 2^3 printf(" 输入: 8\n"); printf(" 预期: 0\n"); printf(" 实际: %d\n", result); printf(" 结果: %s\n", result == 0 ? "通过" : "失败");
if (result == 0) pass_count++; total_count++;
// 测试用例3:边界值1 printf("\n测试3: 边界值1\n"); result = IsPoliteNumber(1); printf(" 输入: 1\n"); printf(" 预期: 0(不能表示为两个或更多连续正整数之和)\n"); printf(" 实际: %d\n", result); printf(" 结果: %s\n", result == 0 ? "通过" : "失败");
if (result == 0) pass_count++; total_count++;
// 测试用例4:边界值3 printf("\n测试4: 边界值3\n"); result = IsPoliteNumber(3); printf(" 输入: 3\n"); printf(" 预期: 1(3=1+2)\n"); printf(" 实际: %d\n", result); printf(" 结果: %s\n", result == 1 ? "通过" : "失败");
if (result == 1) pass_count++; total_count++;
// 测试用例5:较大的礼貌数 printf("\n测试5: 较大的礼貌数\n"); result = IsPoliteNumber(15); // 15=7+8 或 4+5+6 或 1+2+3+4+5 printf(" 输入: 15\n"); printf(" 预期: 1\n"); printf(" 实际: %d\n", result); printf(" 结果: %s\n", result == 1 ? "通过" : "失败");
if (result == 1) pass_count++; total_count++;
// 测试用例6:质数(通常是礼貌数,除了2) printf("\n测试6: 质数(礼貌数)\n"); result = IsPoliteNumber(7); // 7=3+4 printf(" 输入: 7\n"); printf(" 预期: 1\n"); printf(" 实际: %d\n", result); printf(" 结果: %s\n", result == 1 ? "通过" : "失败");
if (result == 1) pass_count++; total_count++;
// 测试用例7:较大的2的幂次方 printf("\n测试7: 较大的2的幂次方\n"); result = IsPoliteNumber(32); // 32=2^5 printf(" 输入: 32\n"); printf(" 预期: 0\n"); printf(" 实际: %d\n", result); printf(" 结果: %s\n", result == 0 ? "通过" : "失败");
if (result == 0) pass_count++; total_count++;
// 测试用例8:大数测试 - 礼貌数 printf("\n测试8: 大数测试 - 礼貌数\n"); start = clock(); result = IsPoliteNumber(1000000); // 1000000是礼貌数 end = clock(); cpu_time_used = ((double) (end - start)) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC * 1000; // 转换为毫秒
printf(" 输入: 1000000\n"); printf(" 预期: 1\n"); printf(" 实际: %d\n", result); printf(" 运行时间: %.2f 毫秒\n", cpu_time_used);
// 检查结果和运行时间 int time_check = (cpu_time_used > 0.1); // 运行时间应大于0.1毫秒 int result_check = (result == 1);
if (result_check && time_check) { printf(" 结果: 通过(结果正确且使用了循环)\n"); pass_count++; } else if (result_check && !time_check) { printf(" 结果: 失败(结果正确但运行时间过短,可能使用了直接判断)\n"); } else { printf(" 结果: 失败(结果错误)\n"); } total_count++;
// 测试用例9:大数测试 - 非礼貌数 printf("\n测试9: 大数测试 - 非礼貌数\n"); start = clock(); result = IsPoliteNumber(1048576); // 1048576=2^20,不是礼貌数 end = clock(); cpu_time_used = ((double) (end - start)) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC * 1000; // 转换为毫秒
printf(" 输入: 1048576\n"); printf(" 预期: 0\n"); printf(" 实际: %d\n", result); printf(" 运行时间: %.2f 毫秒\n", cpu_time_used);
// 检查结果和运行时间 time_check = (cpu_time_used > 0.1); // 运行时间应大于0.1毫秒 result_check = (result == 0);
if (result_check && time_check) { printf(" 结果: 通过(结果正确且使用了循环)\n"); pass_count++; } else if (result_check && !time_check) { printf(" 结果: 失败(结果正确但运行时间过短,可能使用了直接判断)\n"); } else { printf(" 结果: 失败(结果错误)\n"); } total_count++;
// 汇总结果 printf("\n=== 测试结果 ===\n"); printf("通过: %d/%d (%.1f%%)\n", pass_count, total_count, (float)pass_count / total_count * 100);
if (pass_count == total_count) { printf("所有测试通过!\n"); } else { printf("有 %d 个测试失败\n", total_count - pass_count); }
// 特别说明 if (pass_count >= 7 && pass_count < total_count) { printf("\n注意:部分测试失败可能是因为使用了直接判断方法(检查2的幂次方)。\n"); printf("本题要求必须使用循环实现,请检查您的实现方法。\n"); }}
int IsPoliteNumber(int n){ int test = n, sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= test; i++) { for (int j = i; j < test; j++) { sum += j; if (sum == test) { return 1; } else if (sum > test) { break; } } sum = 0; } return 0;}TestMatrixTranspose.c
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>
// 函数原型声明int** TransMat(int** matrix, int m, int n);int** CreateMatrix(int m, int n);void FreeMatrix(int** matrix, int m);void PrintMatrix(int** matrix, int m, int n);int CompareMatrices(int** mat1, int m1, int n1, int** mat2, int m2, int n2);void RunTests();
int main(){ RunTests(); printf("\n测试完成,按任意键退出..."); getchar(); return 0;}
// 创建指定大小的矩阵并填充测试数据int** CreateMatrix(int m, int n){ if (m <= 0 || n <= 0) return NULL;
int** matrix = (int**)malloc(m * sizeof(int*)); if (matrix == NULL) return NULL;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) { matrix[i] = (int*)malloc(n * sizeof(int)); if (matrix[i] == NULL) { // 分配失败,释放已分配的内存 for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) { free(matrix[j]); } free(matrix); return NULL; }
// 填充测试数据:matrix[i][j] = i * n + j + 1 for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) { matrix[i][j] = i * n + j + 1; } }
return matrix;}
// 释放矩阵内存void FreeMatrix(int** matrix, int m){ if (matrix == NULL) return;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) { free(matrix[i]); } free(matrix);}
// 打印矩阵void PrintMatrix(int** matrix, int m, int n){ if (matrix == NULL) { printf("矩阵为空\n"); return; }
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) { printf("%4d", matrix[i][j]); } printf("\n"); }}
// 比较两个矩阵是否相等int CompareMatrices(int** mat1, int m1, int n1, int** mat2, int m2, int n2){ if (m1 != m2 || n1 != n2) return 0; if (mat1 == NULL || mat2 == NULL) return 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m1; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < n1; j++) { if (mat1[i][j] != mat2[i][j]) { return 0; } } } return 1;}
// 测试函数void RunTests(){ printf("=== 矩阵转置函数测试 ===\n\n");
int pass_count = 0; int total_count = 0;
// 测试用例1:2x3矩阵转置 printf("测试1: 2x3矩阵转置\n"); int** original1 = CreateMatrix(2, 3); printf("原始矩阵(2x3):\n"); PrintMatrix(original1, 2, 3);
int** result1 = TransMat(original1, 2, 3); printf("转置结果(3x2):\n"); PrintMatrix(result1, 3, 2);
// 验证结果:创建期望的转置矩阵 int** expected1 = CreateMatrix(3, 2); if (expected1 != NULL) { expected1[0][0] = 1; expected1[0][1] = 4; expected1[1][0] = 2; expected1[1][1] = 5; expected1[2][0] = 3; expected1[2][1] = 6; }
int test1_pass = CompareMatrices(result1, 3, 2, expected1, 3, 2); printf("结果: %s\n\n", test1_pass ? "通过" : "失败");
if (test1_pass) pass_count++; total_count++;
// 释放内存 FreeMatrix(original1, 2); FreeMatrix(result1, 3); FreeMatrix(expected1, 3);
// 测试用例2:1x1矩阵转置 printf("测试2: 1x1矩阵转置\n"); int** original2 = CreateMatrix(1, 1); printf("原始矩阵(1x1):\n"); PrintMatrix(original2, 1, 1);
int** result2 = TransMat(original2, 1, 1); printf("转置结果(1x1):\n"); PrintMatrix(result2, 1, 1);
int test2_pass = (result2 != NULL) && (result2[0][0] == original2[0][0]); printf("结果: %s\n\n", test2_pass ? "通过" : "失败");
if (test2_pass) pass_count++; total_count++;
// 释放内存 FreeMatrix(original2, 1); FreeMatrix(result2, 1);
// 测试用例3:3x1矩阵转置(列向量) printf("测试3: 3x1矩阵转置(列向量)\n"); int** original3 = CreateMatrix(3, 1); printf("原始矩阵(3x1):\n"); PrintMatrix(original3, 3, 1);
int** result3 = TransMat(original3, 3, 1); printf("转置结果(1x3):\n"); PrintMatrix(result3, 1, 3);
// 验证结果 int test3_pass = 1; if (result3 != NULL) { test3_pass = (result3[0][0] == 1) && (result3[0][1] == 2) && (result3[0][2] == 3); } else { test3_pass = 0; } printf("结果: %s\n\n", test3_pass ? "通过" : "失败");
if (test3_pass) pass_count++; total_count++;
// 释放内存 FreeMatrix(original3, 3); FreeMatrix(result3, 1);
// 测试用例4:1x4矩阵转置(行向量) printf("测试4: 1x4矩阵转置(行向量)\n"); int** original4 = CreateMatrix(1, 4); printf("原始矩阵(1x4):\n"); PrintMatrix(original4, 1, 4);
int** result4 = TransMat(original4, 1, 4); printf("转置结果(4x1):\n"); PrintMatrix(result4, 4, 1);
// 验证结果 int test4_pass = 1; if (result4 != NULL) { test4_pass = (result4[0][0] == 1) && (result4[1][0] == 2) && (result4[2][0] == 3) && (result4[3][0] == 4); } else { test4_pass = 0; } printf("结果: %s\n\n", test4_pass ? "通过" : "失败");
if (test4_pass) pass_count++; total_count++;
// 释放内存 FreeMatrix(original4, 1); FreeMatrix(result4, 4);
// 测试用例5:方阵转置(3x3) printf("测试5: 3x3方阵转置\n"); int** original5 = CreateMatrix(3, 3); printf("原始矩阵(3x3):\n"); PrintMatrix(original5, 3, 3);
int** result5 = TransMat(original5, 3, 3); printf("转置结果(3x3):\n"); PrintMatrix(result5, 3, 3);
// 验证方阵转置:对角线不变,其他元素对称交换 int test5_pass = 1; if (result5 != NULL) { for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) { if (result5[i][j] != original5[j][i]) { test5_pass = 0; break; } } if (!test5_pass) break; } } else { test5_pass = 0; } printf("结果: %s\n\n", test5_pass ? "通过" : "失败");
if (test5_pass) pass_count++; total_count++;
// 释放内存 FreeMatrix(original5, 3); FreeMatrix(result5, 3);
// 汇总结果 printf("=== 测试结果汇总 ===\n"); printf("通过测试: %d/%d\n", pass_count, total_count); printf("成功率: %.1f%%\n", (float)pass_count / total_count * 100);
if (pass_count == total_count) { printf("🎉 所有测试通过!\n"); } else { printf("❌ 有 %d 个测试失败\n", total_count - pass_count); }}
int** TransMat(int** matrix, int m, int n){ int **arr; arr = (int **)malloc(n * sizeof(int *)); for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { arr[i] = (int *)malloc(m * sizeof(int)); if(arr[i] == NULL) return NULL; for(int j = 0; j < m; j++) { arr[i][j] = matrix[j][i]; } } return arr;}文章分享
如果这篇文章对你有帮助,欢迎分享给更多人!
2025.12.02 C语言程序设计上机实习五
https://mjy.js.org/posts/20251202-c语言程序设计上机实习五/ 
